Digital instruments are a way of thematizing man-machine coupling and co-development, focusing on mediation.
-
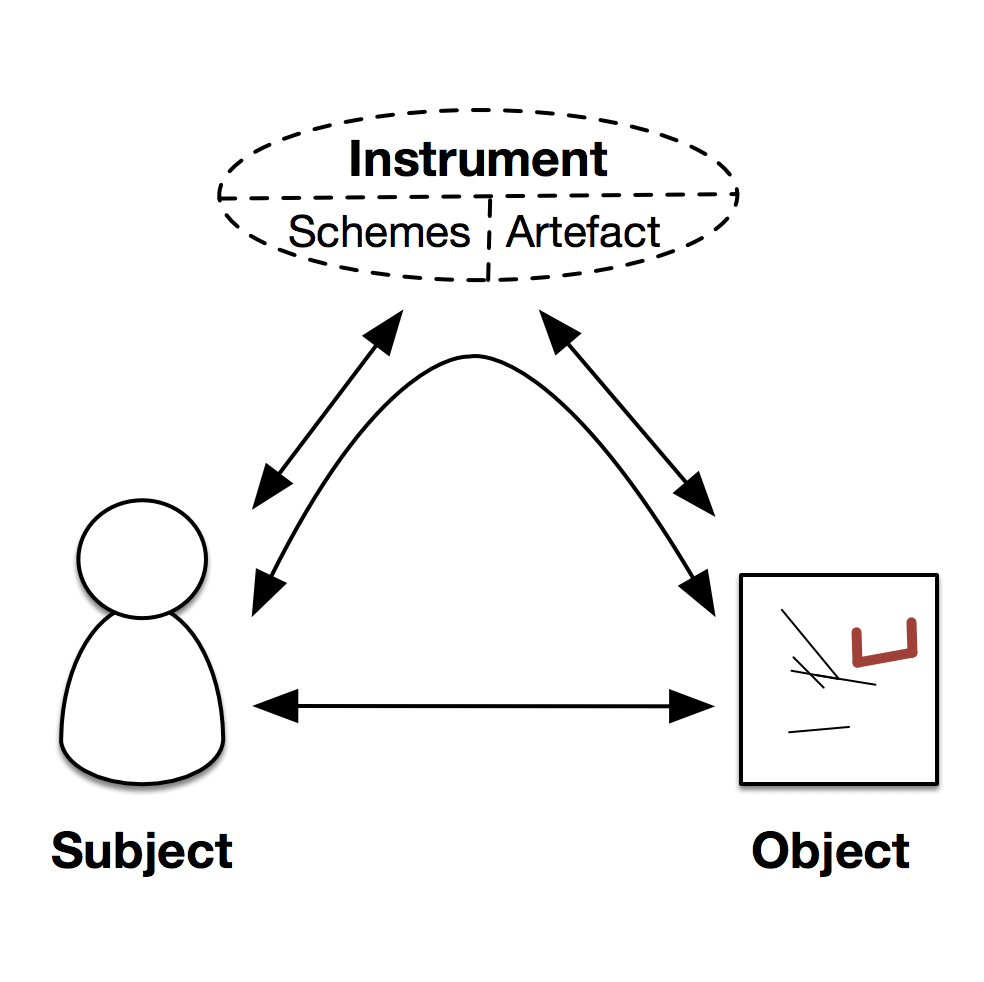
DIADEME: Digital Instrument and Activity DEvelopMEnt
Digital Instruments
Experience analysis and modelling
Interpretation Systems
Trace-based Activity Analysis
A small research program around the notion of Digital Instrument, and their co-evolution with humans, mainly related to Amaury Belin PhD thesis, as well as HdR writing. May be reactivated.
Details
Partners: LS2N
Funding: Amaury Belin PhD funding, Atlanstic 2020
Beginning: 2012-10-01
End:
Related publications
-
Amaury Belin, Yannick Prié, Aurélien Tabard. (2014) Supporting the Development of Digital Skills in Digital Intelligence, Nantes, France, sept 2014. Show abstract In a world where activities, goals and available software are rapidly changing, users must constantly adapt. In this position paper, we discuss how digital skills are different from traditional skills due to their highly dynamic na-ture, both in the tools used and the tasks to be carried out. We advocate the needs both for interdisciplinary theory to conceptualize digital skill develop-ment, and for longitudinal, large-scale and trace-based methods to observe such phenomenon. We illustrate how digital tools could better support users in the development of skills, highlighting how traces of interaction could be leveraged within reflective and skill-sharing tools.
-
Amaury Belin, Antipov Grigory, Julien Blanchard, Fabrice Guillet, Yannick Prié. (2014) Mining Users Skills Development From Interaction Traces: an exploratory study in Atelier Fouille visuelle de données temporelles, IHM 2013, Nov 2014, Bordeaux, France. 2p, 2014 Show abstract In this paper, we report an exploratory work related to the detection of user skills development from large interactions traces. We present a statistical approach to tackle the development of user's low level skills by identifying patterns of action and studying their progressive automations (i.e. as a user develops skills, they execute common subsequent actions faster) as well as their evolutions (i.e. user elaborating innovative ways to achieve a common task).
-
Amaury Belin, Yannick Prié. (2012) Towards a model for describing appropriation processes through the evolution of digital artifacts in Designing Interactive Systems DIS2012, pp. 645-654, Newcastle, June 2012. [AR:20%] doi Show abstract Appropriation of technology is a process by which users complete the work of designers by making interactive systems functional within the frame of their situated activities. While existing theories and studies about appropriation are oriented toward the psychological or organizational dimension of this process, we propose a model to describe it through evolutions of digital artifacts and information structures. We also present a case study demonstrating how this model helps to identify particular user operations, and related digital transformations, as a part of the appropriation process. These findings open perspectives to bridge scattered theoretical approaches of appropriation around a low-level, artifact-oriented, and objective way of describing appropriation. Our model could also improve the way appropriation is taken into account in design, by bringing more focus on technical aspects of interactive systems.
-
Yannick Prié. (2011) Vers une phénoménologie des inscriptions numériques. Dynamique de l’activité et des structures informationnelles dans les systèmes d’interprétation in Habilitation à Diriger des Recherches en Informatique, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, Nov 2011, 247 p. (Soutenue le 18 novembre 2011 à l'Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1 - Laboratoire LIRIS - UMR 5205 CNRS - École Doctorale Informatique et Information pour la Société) This study is mandatory to get a Professor position in France. The document is entitled Towards a Phenomenology of Digital Inscriptions. Dynamics of Activity and Informational Structures in Interpretation Systems. In the first chapter I first study the notion of inscription of knowledge as proposed by Bruno Bachimont. As I consider it is not sufficiently tied with human action and activity as considered by post-cognitivist theories, I propose to consider the notion of informational structures (structures informationnelles). Informational structures are digital inscriptions of knowledge that are actually manipulated by subjects during their computer-mediated activity, they can be canonical (explicitely manipulated by the system) or non canonical (but as such, they can become canonical if reified). The notion of informational structure is useful to study how digital inscriptions and activity are interwoven at different analysis levels, it is associated to the notion of information space that users enact during their activities, and enables to study at the individual level what could be called a phenomenology of digital inscriptions. In the second chapter of the document, I focus on explicit information spaces that users enact during knowledge work, and detail the notions of interpretation systems within which inscriptions of knowledge circulate. I present my work on video active reading and the Advene project. In the third chapter, I propose to define traces as inscriptions that are used during an activity as signs of the past, and I discuss the notion of interpretation systems that are dedicated to traces. I present my work on such systems, along first the Musette (Modelling Users and Tasks to Traces Experience) approach and then the mTBS (Modelled Trace-Based systems) approach.
Examination committee: Nathalie Aussenac (Directeur de Recherche, CNRS, Toulouse; referee), Bruno Bachimont (Enseignant-Chercheur HDR, UT Compiè̀gne; referee), Sylvie Leleu-Merviel (Professeur, Université de Valenciennes; referee), Michel Beaudouin-Lafon (Professeur, Université Paris-Sud; examiner), Catherine Garbay (Directeur de Recherche, CNRS, Grenoble; examiner), Alain Mille (Professeur, Université Lyon 1; examiner), Pascal Salembier (Professeur, UT Troyes; examiner). Show abstract Ce mémoire est l'occasion de présenter nos travaux à l'Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1. Il est composé de trois parties, la première visant à proposer une thématisation originale des liens entre activité et inscriptions numériques de l'activité sous la forme de structures informationnelles, les deux suivantes étant consacrées à nos thématiques principales de recherche qui sont, d'une part la lecture active audiovisuelle et les systèmes d'interprétation, et d'autre part les systèmes à base de traces modélisées.
Le premier chapitre est consacré à l'exploration des liens entre l'activité informatiquement médiée et les représentations qui y sont impliquées. Une première étude critique décrit la notion d'inscription de connaissances proposée par B. Bachimont au sein d'une théorie du support pour permettre de penser la rencontre ou l’expérience qu’une conscience fait des dispositifs technologiques et des inscriptions. Cette proposition vise à thématiser la numéricité des inscriptions et nous intéresse donc à ce titre, mais elle se révèle à notre sens insuffisante pour penser un individu actif engagé dans un processus de manipulation d'inscriptions. Une seconde étude est alors consacrée aux liens entre action, activité et inscriptions dans les théories dites « post-cognitivistes » de la cognition. Les inscriptions soutiennent l'activité et la sous-tendent tout à la fois, et nous nous intéresserons particulièrement aux inscriptions dans leur perception et leur manipulation par un être humain suivant la théorie instrumentale. Cependant, les inscriptions en tant qu'elles peuvent être numériques ne sont que peu thématisées. Notre dernière étude est orientée autour de la proposition de penser la notion de structure informationnelle et les instruments associés comme permettant d'articuler le monde numérique à l'activité humaine et l'activité humaine au monde numérique. Une structure informationnelle est une inscription numérique en acte, objectivable, mais non obligatoirement canonique, c'est-à-dire manipulée explicitement par le système. Cette proposition permet de penser le côté humain de l'activité instrumentée tout en conservant le calcul et les représentations associées comme préoccupation informatique. Nous présentons également la notion d'espace informationnel qu'un utilisateur énacte, et les directions de recherche ouvertes par nos propositions.
Le deuxième chapitre est principalement consacré à la présentation de nos travaux sur les systèmes de lecture active audiovisuelle. Nous proposons d'abord une étude rapide sur le cadre général des technologies intellectuelles comme soutenant le travail intellectuel, l'activité ouverte d'interprétation et de manipulation d'inscriptions de connaissances personnelles. De telles inscriptions et réinscriptions se font au sein de ce que nous proposons d'appeler des systèmes d'interprétation qui offrent aux utilisateurs la possibilité de manipuler consciemment des structures informationnelles de toutes sortes, par exemple sous la forme de données, de schémas ou de feuilles de style et de formulaires, et de partager celles-ci comme réifications de pratiques. La lecture active audiovisuelle est une activité intellectuelle qui s'effectue dans un système d'interprétation permettant de construire des hypervidéos à partir d'annotations. Nous présentons alors nos travaux autour du projet Advene (Annotate Digital Video, Exchange on the NEt), notamment les modèles associés, l'outil générique Advene pour l'annotation et la construction d'hypervidéos, ainsi que quelques applications de lecture active associées à l'analyse des interactions et la critique filmique. Nous pouvons alors tirer un bilan des presque dix ans de ce projet et proposer quelques directions pour la suite.
Le troisième et dernier chapitre présente essentiellement nos travaux sur les traces numériques. Nous définissons d'abord la notion de trace en général comme inscription permettant de viser le passé au cours d'une interprétation et présentons comment les traces d'activité médiées sont largement utilisées au sein de systèmes variés allant de l'analyse à la réflexivité. Nous considérons que l'enjeu est de manipuler des traces numérique explicites définies comme « inscriptions canoniques temporellement orientées » dans des systèmes d'interprétation orientés trace. Nous pouvons alors présenter la notion de trace modélisée comme un certain type de trace explicite, ainsi que nos travaux dans ce cadre depuis plus de dix ans : l'approche Musette, le cadre général des systèmes de base de traces modélisées (SBTm) ainsi que la formalisation des traces et des transformations pour construire des systèmes de gestion de bases de traces (SGBT). Différents travaux applicatifs sont ensuite présentés qui permettent d'illustrer les différentes utilisations des traces modélisées dans des contextes applicatifs variés, visant notamment le support à l'awareness, à la remémoration, à la réflexivité, à la redocumentation et au partage, ou encore à la reprise d'activité.
Related software
-
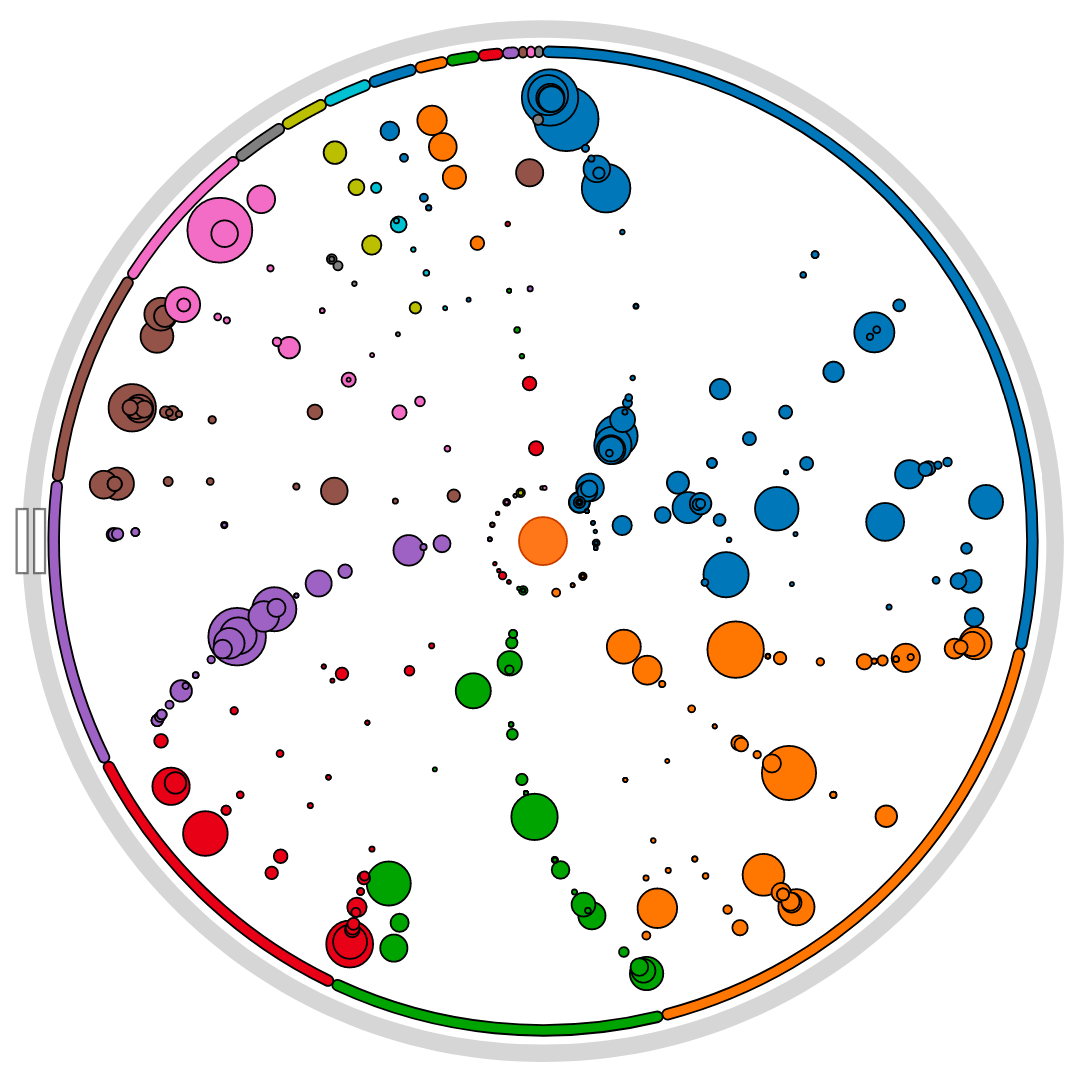
EPISTEME: Transdisciplinary epistemology of digital technologies
Data Visualization
Digital Instruments
Interpretation Systems
Reflective Systems
Trace-based Activity Analysis
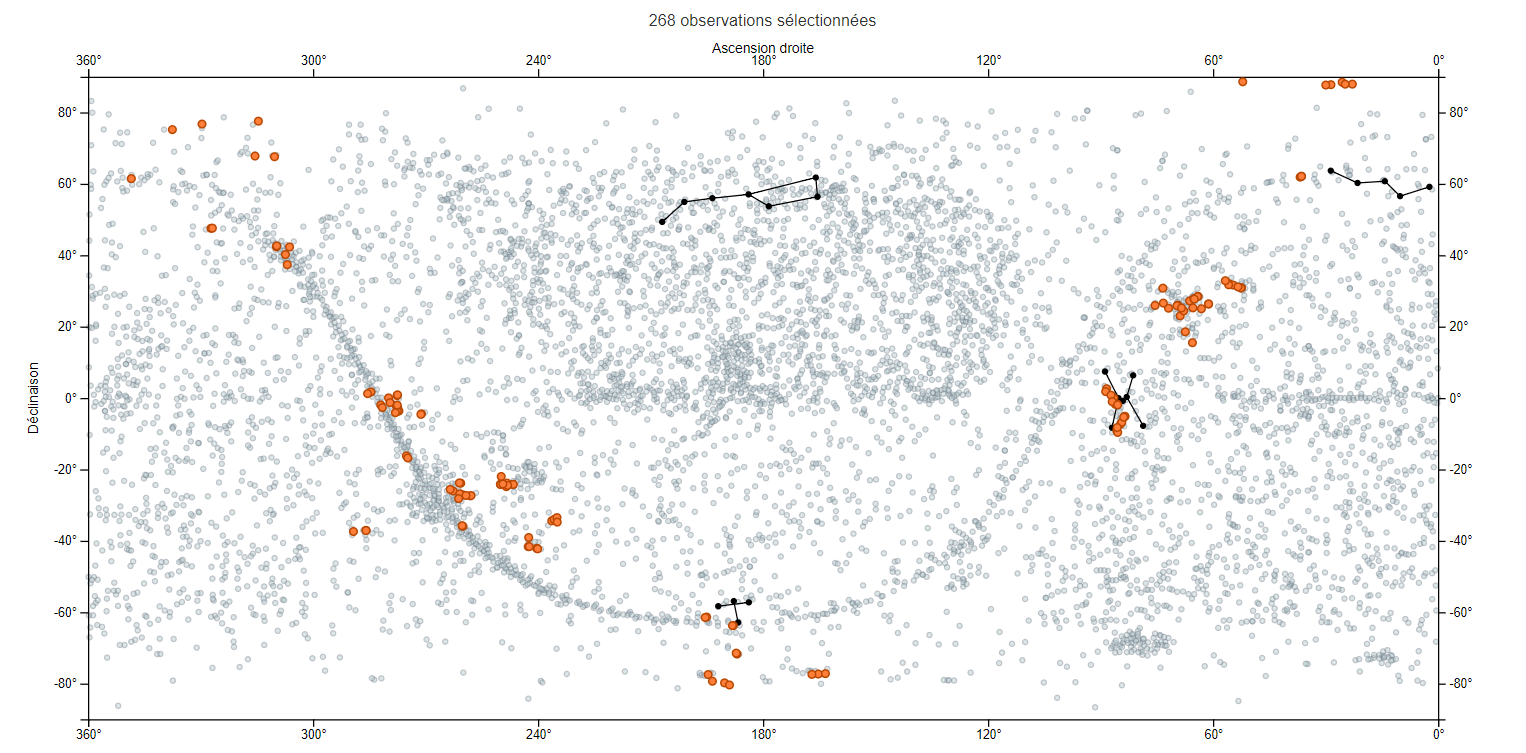
Work on data analysis of astrophysical research activity, producing datavisualizations that highligh different processes related to observations, the organization of working groups, as well as the software "black boxes".
Details
Partners: IRI Centre Pompidou, LINA, LIRIS, CHS Paris 1, CEA Irfu, France Televisions, Mediapart
Funding: French National Research Agency (ANR)
Beginning: 2014-10-01
End: 2018-02-28
Website: https://projet-episteme.org/
Additional comments
The aim of this transdisciplinary program EPISTEME is first to identify the most characteristic aspects of the transformation of two chosen disciplines (astrophysics, history) in their relations to their objects under the effect of digital formalization. The other goal is to design instruments for the scientific communities of peers that allow contributive categorization, to support debates and controversies, based on the concept of transindividuation, and to articulate bottom-up -stemming from individual research activities- and top down processes -more or less local, laboratory-, school- or discipline-wide certification processes from peer community debates.
We developed the Herschel Mission Explorer. We are currently working on a second version that will feature a general design overhaul.
Additional illustrations
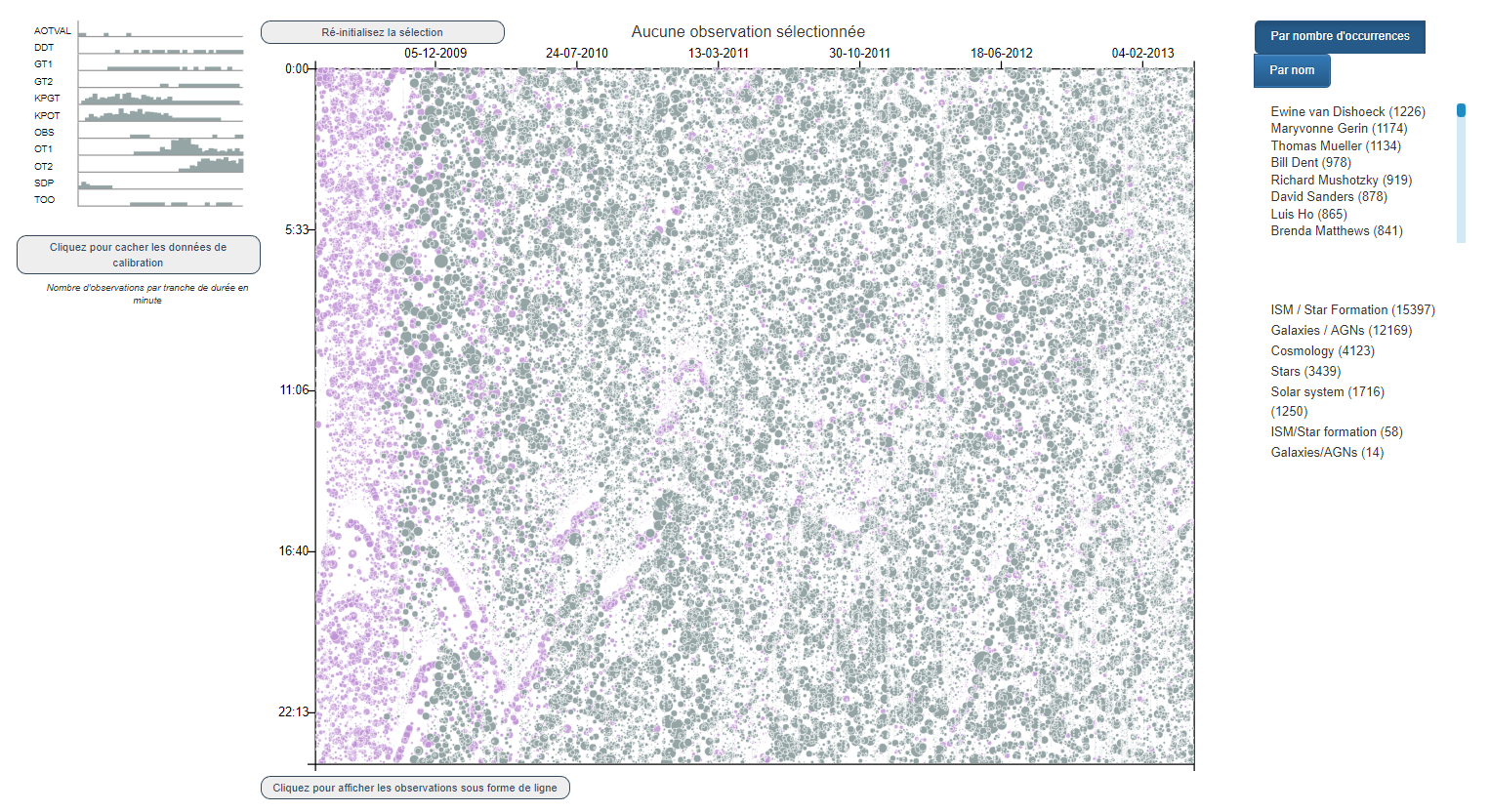
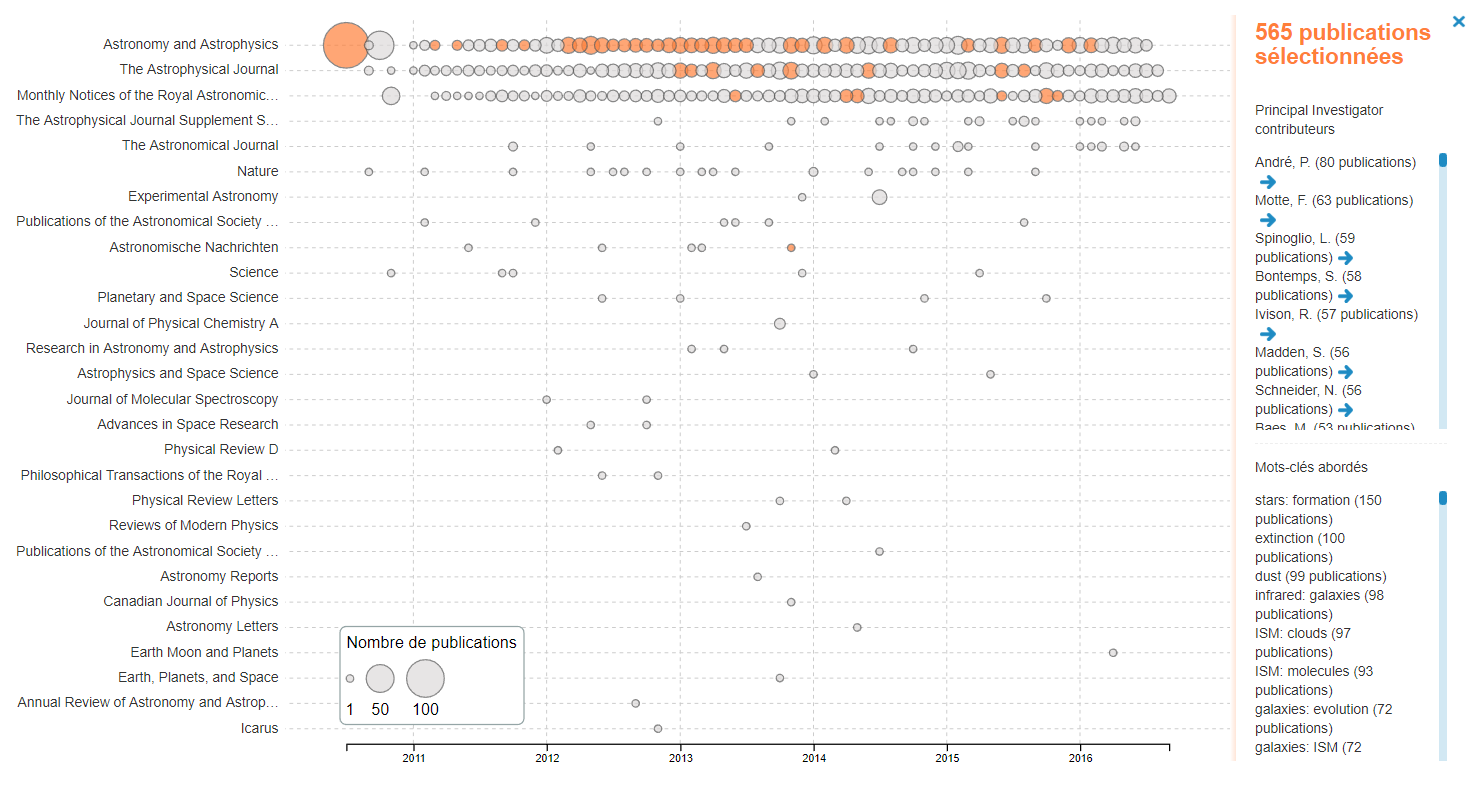
Select another theme:
Accessibility
Affordances
Data Visualization
Digital Instruments
Document Engineering
Experience analysis and modelling
Hypervideos
Immersive Analytics
Interpretation Systems
Knowledge Engineering
Learning Analytics
Patient Experience
Progressive analytics
Reflective Systems
Technology-Enhanced Learning
Trace-based Activity Analysis
Trace-based Systems
VR and Psychotherapy
Video Annotations
Virtual Reality





